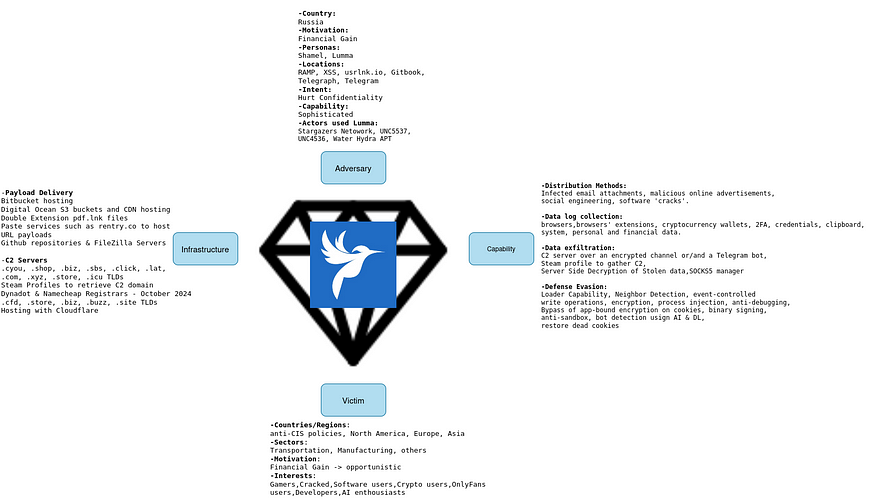
In this blog, we analyze the evolution of Lumma in 2024, based on the Diamond Model vertices.
Disclaimer: Everything stated in this blog is for informational purposes only, with no intention of promoting the use of these products.
Key Points
- Lumma is a professional-grade information stealer marketed as Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS), targeting credentials, cryptocurrency wallets, browser data, and 2FA details, with advanced features like binary morphing and server-side data decryption.
- The malware’s subscription-based plans — Experienced, Professional, and Corporate — offer varying levels of log management, data filtering, and customization, with the highest tier focusing on stealth and advanced security bypass techniques.
- Lumma’s developers enforce “anti-CIS” policies, refusing to target Russia or accept offers to bypass this restriction, and maintain a strong presence on Russian-speaking forums while engaging with clients via Telegram and Gitbook resources.
- Observations reveal frequent campaigns throughout 2024 targeting sectors like manufacturing and transportation, as well as individuals like gamers, cracked software users, and cryptocurrency enthusiasts, with tactics including phishing and malvertising.
- The article highlights Lumma’s dominance in the stealer market, noting its extensive distribution efforts, potential for law enforcement attention, and the benefit for defenders in focusing on well-known malware for evolving detection strategies.
Adversary
Lumma (aka LummaC2, Lummac and Lumma Stealer) is an advanced information-stealing Malware-as-a-Service (MaaS) with Russian origins, observed in the wild since 2022. It is marketed as a “professional-grade” tool that can extract sensitive data from Windows 7 x32 to Windows 11 x64 . Written in C and providing customizable functionality, it primarily targets cryptocurrency wallets, browser cookies & extensions, credentials, credit card information and two-factor authentication (2FA) details, before ultimately stealing sensitive information from compromised machines.
Lightweight and stealthy, it avoids detection through techniques like binary morphing (changing its code to evade antivirus tools) and low-level system interactions. It is subscription-based, offering various plans with features such as bulk log downloads, data filtering, and custom data collection profiles. Lumma’s infrastructure relies on powerful servers with encryption and anti-DDoS protection, and updates are provided frequently to ensure it remains effective. The malware is managed via an easy-to-use interface, making it accessible even to less technically skilled users.

In just 2 years of existence Lumma has already managed to become the most tracked malware:



Lumma developers operate a usrlnk.io url providing links for their distinct services:

- A Telegram bot for selling their services.
- A Telegram bot for reporting bugs.
- A Telegram bot for selling/acquiring Lumma Logs.

Of course, operators can still monetize the stolen logs on undergound forums or sell credentials with valid access to organizations (Initial Access Brokers – IABs):

- A Gitbook (also available in telegra.ph) that offers detailed documentation and FAQs for their product, containing information regarding the stealer, its features and how-to-use guides.

Lumma offers three subscription plans catering to different levels of usage:
- Experienced ($250/month): This basic plan allows users to set up to 10 filters for log management, download logs in bulk, and search logs by specific queries (e.g., wallets or specific websites). It includes tools to analyze logs by country, currency, or custom filters, and lets users clear logs and track log quality. Users can tag up to three custom builds.
- Professional ($500/month): This intermediate plan includes all features of the Experienced plan, but with unlimited filters and more advanced tools. It enables bulk deletion of logs, statistics sharing, and access to widgets for log quality and filtering. Users can create and customize profiles for data collection, adding or removing browsers, extensions, or file paths. It allows real-time editing of collection rules, the use of masks or variable paths, and deeper customization of the data collection process. The plan also includes a non-residential loader for loading various files with the stealer.
- Corporate ($1,000/month): This premium plan provides all the Professional features with added benefits for better stealth and reliability. Builds are cleaned more frequently and include improved bypass techniques for security defenses, like avoiding detection when accessing password stores. Google account session validity is enhanced through specialized cookies. Builds are morphed into unique variations for better survivability. This plan is ideal for highly targeted operations requiring advanced security and customization.

Lumma is believed to have been developed by the threat actor persona “Shamel”, under the the alias “Lumma”. Lumma has a strong presence on Russian-speaking forums such as RAMP and XSS, to promote their product and its updates:

The researcher g0njxa, on November 2023 conducted a notable HUMINT collection by interviewing Lumma. The following points were notable:
- Overview of Lumma
- Lumma describes itself as one of the most technologically advanced stealers, claiming its innovations are often emulated by competitors.
- Continuous product improvement is a key focus, with steady client growth since its launch on December 21, 2022.
2. Client Base:
- Lumma boasts approximately 400 active clients, which is considered a significant customer base for malware projects. (Lumma and its logs have been used by threat actors such as the Stargazers Ghost Network, UNC5537, UNC4536 and Water Hydra APT)
- Many clients reportedly migrate from competitors like Redline and Meta stealers.
3. June 2023 Update
- A major update including 25 enhancements in June 2023 marked a turning point, significantly increasing Lumma’s use and recognition.
4. Unique Features and Branding
- Lumma incorporates cultural elements, such as Russian and Western poetry, into its infrastructure (e.g., Yesenin and Baudelaire poems on C2 domains), though these have since been removed.
5. Market Trends and Future Plans
- Lumma’s developers acknowledge ongoing demand in the stealer market, with plans to remain active for at least the next 2–3 years.
6. Anti-CIS Policies
- Lumma enforces strict “anti-CIS” policies, refusing to target Russians and rejecting lucrative offers to bypass this restriction.
- The architecture is designed to prevent modification that could enable targeting CIS countries, contrasting with incidents like the WhiteSnake Stealer breach.
7. Response to Tracking Efforts
- Developers are aware of security researchers tracking Lumma and see it as beneficial publicity, highlighting a nonchalant stance toward monitoring.
Capability
Lumma’s capabilities have been well documented by their telegra.ph website and other credible organizations (i.e. any.run, CYFIRMA, SOCRadar, TrendMicro). However, some key TTPs include:
- Distribution Methods: Infected email attachments, malicious online advertisements, social engineering, software ‘cracks’.
- Data log collection: Lumma collects detailed data logs from compromised endpoints, including information extracted from browsers and cryptocurrency wallets.
- Data exfiltration: The malware effectively gathers sensitive information from targeted applications, including login credentials, financial data, and personal details. The data are exfiltrated to the C2 server over an encrypted channel. Can also support exfiltration to a Telegram bot.
- Server Side Decryption of Stolen data: All data transmitted by the stealer is decrypted on the server side, which makes it more difficult to analyze the malware’s traffic during the exfiltration process.
- Loader capability: The stealer can drop additional malware onto compromised machines, expanding its malicious capabilities and potential impact.
- Defense Evasion: Event-controlled write operations, encryption, process injection, anti-debugging
- Neighbor Detection: Lumma notifies operators about other instances of the malware running on the same system.
However, it is of great importance to mention that Lumma receives updates & features on a regular basis that improve and expand its functionality:
December 2024
- Cryptocurrencies clipper module
November 2024
- Multiple updates & bug fixes
October 2024
- Bypass of app-bound encryption on cookies implemented by popular browsers
- Singed Lumma payload in the wild
August 2024
- New config delivery method for C2 addresses via user names of Steam
accounts. The C2 address is obtained by ROT-15 decrypting the user name
July 2024
- Added Any.run sandbox check
May 2024
- Collection of valuable information from Mozilla-based browsers extensions
- Added support for Windows XP on their builds — ref
April 2024
- Implemented a “bot” (researchers, sandboxes, etc) protection system using artificial intelligence and deep learning, pre-trained on screenshots of known virtual machines
February 2024
- Partnership with “GhostSocks”, a SOCKS5 manager
November 2023
- Ability to restore dead cookies using a key from restore files (applies only to Google cookies)
All these benefits of ease to use, fair prices along with advanced and customizable features, seemed to push actors to highly utilize this information stealer. This can be depicted from the high volume of campaigns publicly reported delivering Lumma throughout the year:
December 2024
- Threat actors are abusing community platforms like YouTube and Discord to promote fake cheats and spread NodeLoader that delivers Lumma
November 2024
- Emmenhtal Loader Uses Scripts to Deliver Lumma and Other Malware
- Lumma is Spread in Youtube descriptions impersonating Game Cheats
- Fake AI image and video generators infect Windows with Lumma
- Lumma Campaign targeting the Transportation sector in North America
October 2024
- Malicious ads push Lumma infostealer via fake CAPTCHA pages
- ClearFake variant (without using the EtherHiding technique) is spreading Lumma via the ClickFix tactic on compromised websites
- Fake crypto game “Cosmo Whales” spotted hosting Lumma and using social engineering to spread throughout Discord communities
- Lumma is pushed from fake (typosquatted) websites impersonating legitimate software vendors such as Postman
September 2024
- Fake League of Legends Download Ads Spread Lumma
- Telegram Group promoting cracked software infected with Lumma
- Lumma spread by phishing notification of false security vulnerability on GitHub projects
- Malvertising Spreading Lumma and targeting Users of Outdated Windows in Europe
- On a hacking forum, a user offered a tool to “check” OnlyFans accounts which was in fact a delivery method for Lumma
August 2024
- GitHub comments abused to push Lumma masked as fixes to issues
- Malvertising spreads NUMOZYLOD delivering Lumma
July 2024
- Exploitation of CVE-2024–21412 (a security bypass vulnerability in Microsoft Windows SmartScreen) to deliver Lumma
- Lumma Packed with CypherIt Distributed Using Falcon Sensor Update Phishing Lure
- Phishing campaign by WaterHydra APT impersonating Medicare Australia
June 2024
- Injecting Lumma to Python Package “crytic-compilers”
- Popup text instructs victims to paste copied script that delivers Lumma into window for administrative PowerShell terminal
- Click-Fix Lumma campaign targeting Chile
May 2024
- Fake Browser Updates delivering BitRAT and Lumma
April 2024
- Multiple fake AV sites hosting Lumma payloads
- Threat Actors Deliver Lumma via YouTube Video Game Cracks
March 2024
- No public reports
February 2024
- A vibrator (USB enabled) was infected with Lumma
January 2024
- YouTube Videos Promoting Cracked Software Distribute Lumma

Infrastructure
Lumma’s operators demonstrate a dynamic approach to adapting their infrastructure, frequently modifying their Tactics, Techniques, and Procedures (TTPs) to bypass restrictions and maintain operational effectiveness. Example observations of infrastructure preferences included:
Payload Delivery
- Bitbucket hosting— December 2024
- Digital Ocean S3 buckets and CDN hosting — October 2024
- Double Extension pdf.lnk files— October 2024
- Paste services such as rentry.co to host URL payloads— August 2024
- Github repositories & FileZilla Servers — January 2024
C2 Servers
- .cyou, .shop, .biz, .sbs, .click, .lat, .com, .xyz, .store, .icu TLDs — December 2024
- Dynadot & Namecheap Registrars — October 2024
- .cfd, .store, .biz, .buzz, .site TLDs — October 2024
- Steam Profiles ROT-15 encrypted text to retrieve C2 domain — August 2024
- Hosting with Cloudflare — March 2024
Victim
Lumma developers and operators are motivated by financial gain, meaning everyone is a potential target. Besides that, as mentioned earlier, Lumma developers enforces strict “anti-CIS” policies, refusing to target Russians and rejecting lucrative offers to bypass this restriction.
Additionally, distinct Lumma campaigns have been reported:
- Campaign targeting the Manufacturing sector in North America – December 2024
- Campaign targeting the Transportation sector in North America — November 2024
- Phishing emails impersonating Github reaching users as part of security vulnerabilities requiring their attention in Italy — September 2024
- Malvertising targetting French and Polish Users — September 2024
- Phishing campaign by WaterHydra APT impersonating Medicare Australia — July 2024
- Exploitation of CVE-2024–21412 to deliver Lumma in North America, Spain, Thailand — July 2024
- Click-Fix campaign targeting Chile — June 2024
Also, based on campaigns themes described in the Capabilities section, the following groups of individuals seems to be targeted:
- Gamers
- Cracked Software users
- Crypto users
- OnlyFans users
- Developers
- AI enthousiasts
Observations/Questions
- Is Lumma so effective that threat actors devote significant time and tradecraft only to design distribution methods? It seems so, given the volume of different campaigns spreading Lumma throughout the year.
- Will Lumma continue to rise in 2025? We’ll see. Being a leader in the cybercrime sector usually attracts law enforcement actions.
- Can we track distinct threat actor groups that utilize Lumma? Possibly, by focusing on distribution efforts and themes, along with build and feature clustering per payload observed. We can leave that to the big players with bigger volumes of telemetry.
- Is it beneficial for defenders that a single malware is so popular among attackers? Probably, since the community is familiar with this malware, and hunting/detection mechanisms are in place and constantly evolving.
- Any predictions for 2025? Similar MaaS could emerge, extremely focused and professional, with regular updates and unique features to compete with other strong players like Lumma and Vidar.
Appendix — Diamond Model